유니티의 물리엔진의 기본 기능들의 샘플 구현
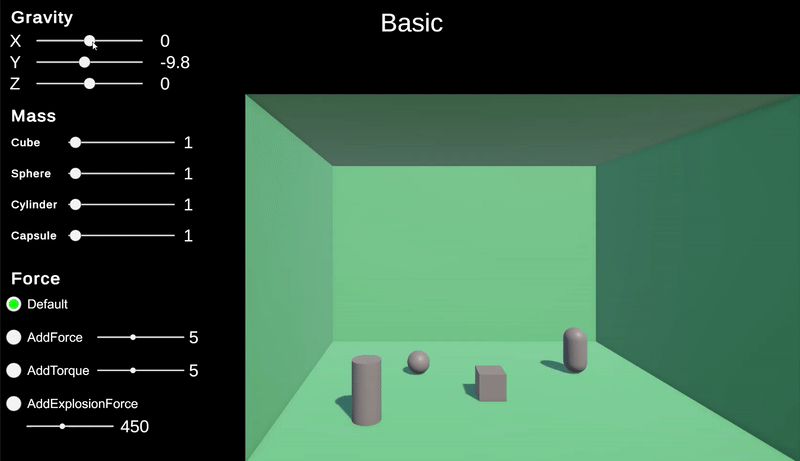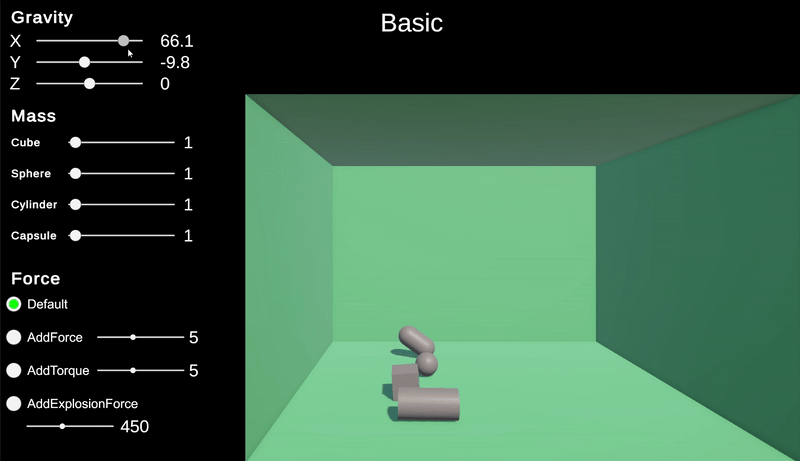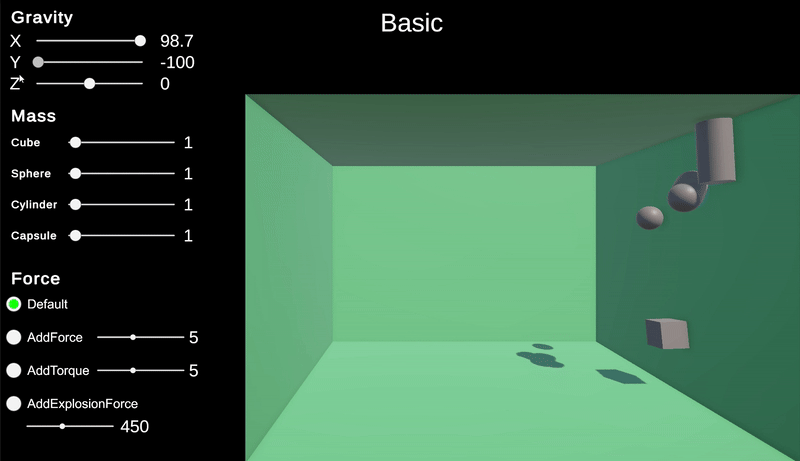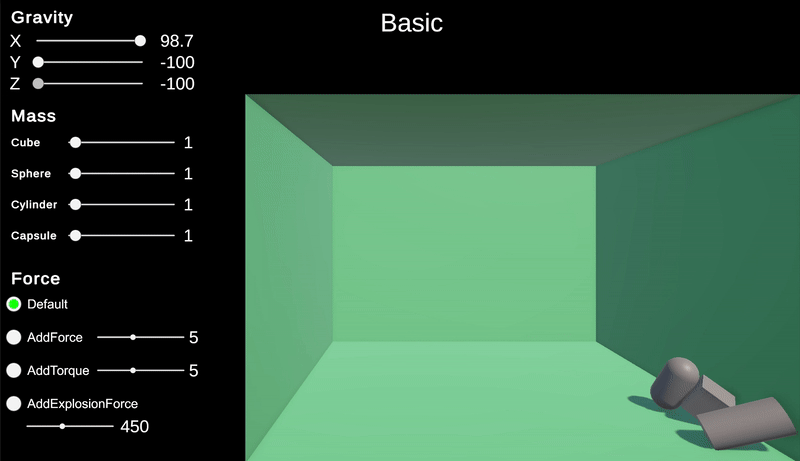
중력
유니티는 물리적인 오브젝트에는 중력과 힘 등의 물리 작용들이 적용된다.
물리적인 오브젝트란 Rigidbody 컴포넌트가 붙어있는 것으로 이 컴포넌트에서 중력의 적용 여부나 질량, 마찰력 등의 설정을 제어할 수 있다.
유니티의 중력은 Physics.gravity로 접근하여 값을 가져오고 변경할 수 있다.
이 중력은 Vector3 값으로 기본값은 현실과 동일하게 y 축으로 -9.81으로 되어있다.
이 값을 변경하면 중력을 다양한 방식으로 적용할 수 있다.
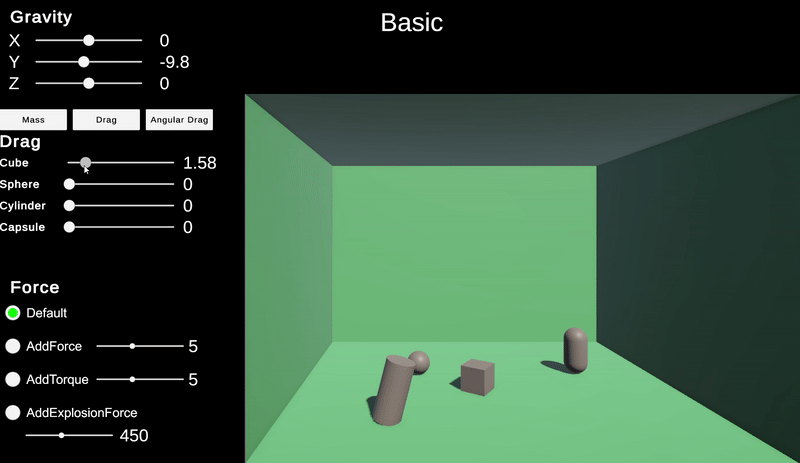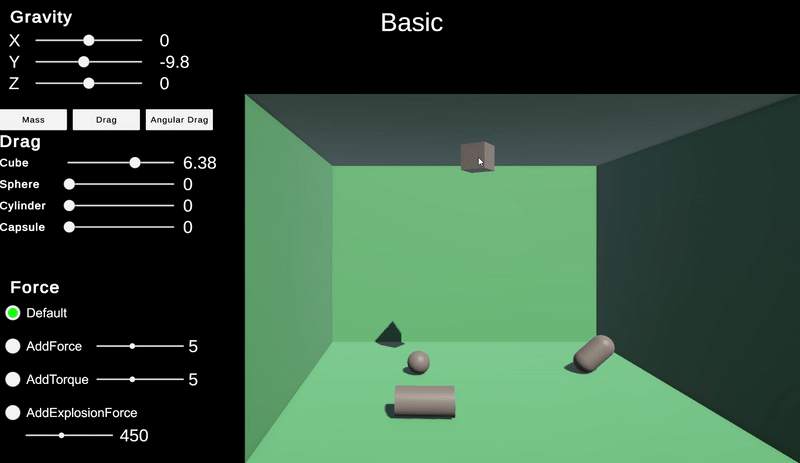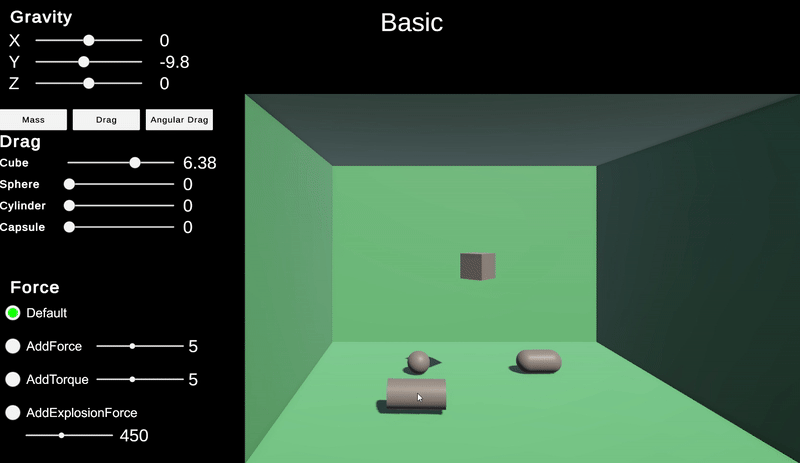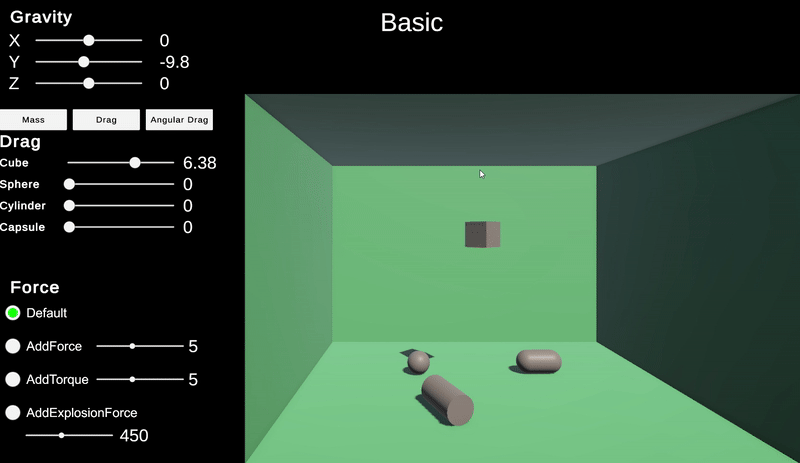
Rigidbody 컴포넌트의 drag 값은 항력을 제어한다. 하지만 이는 선형적인 값으로 현실적인 물리와는 차이가 있다.
angular drag는 회전 항력으로 회전력에 적용되는 저항력이다.

힘
물리적인 상태의 오브젝트에는 힘을 가해서 움직이거나 회전 또는 범위 내 오브젝트에 거리 비례 힘을 가하는 물리 기능들을 사용할 수 있다.
AddForce
물체에 특정 방향으로 특정 크기만큼의 힘을 가한다.

AddTorque
물체에 회전력을 준다.

AddExplosionForce
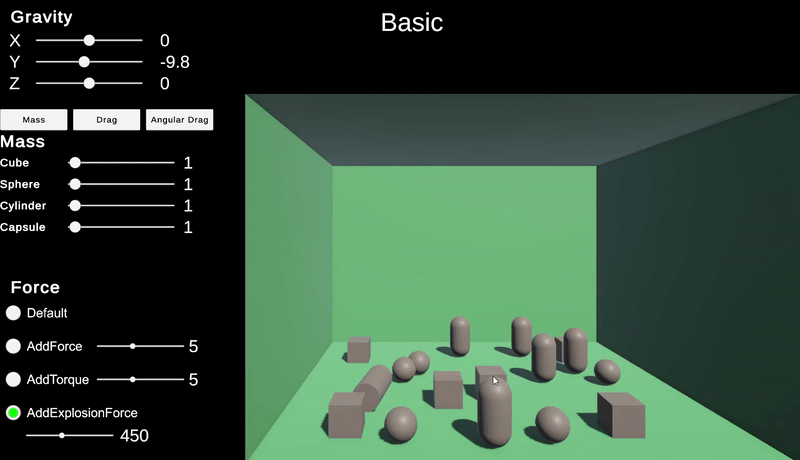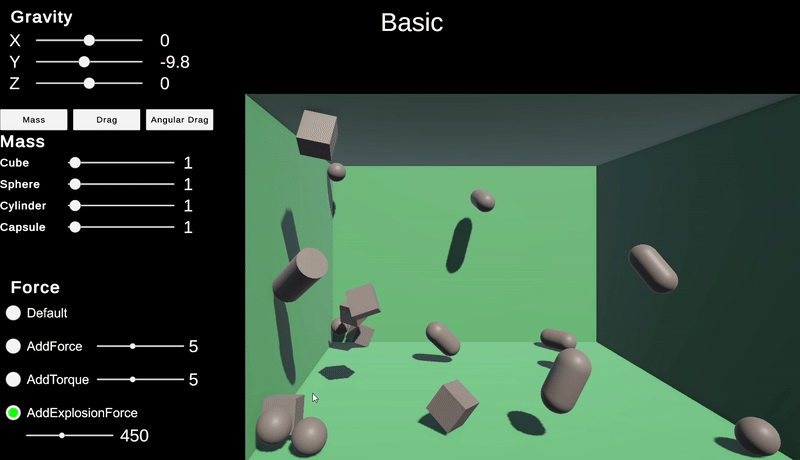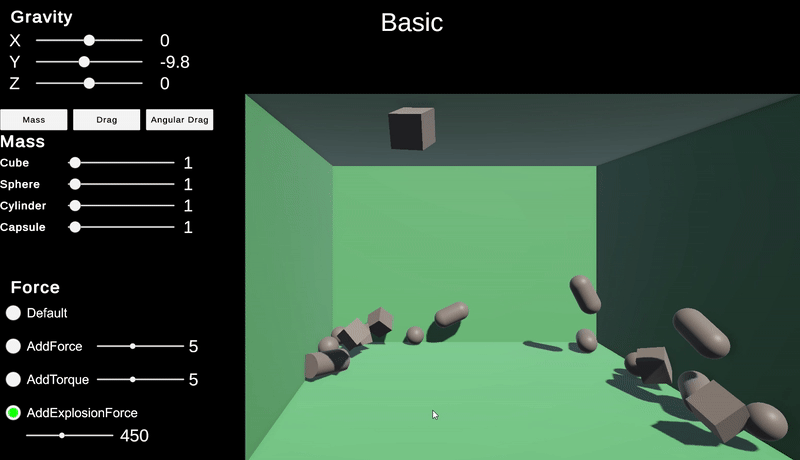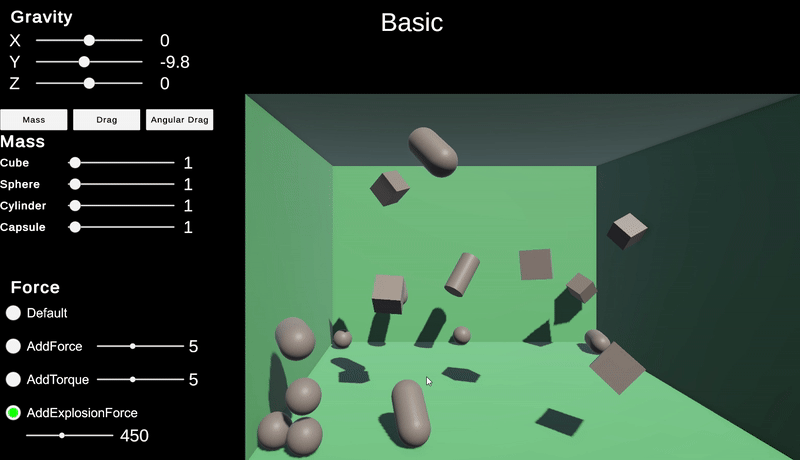
AddExplosionForce는 이 함수만 호출한다고 주변에 영향을 주는 것이 아니라 특정한 객체를 기준으로 영향을 줄 주변 객체를 직접 탐색하면서 AddExpolsionForce를 적용시킨다.
public void ApplyExplosion(float force, float radius)
{
Collider[] colliders = Physics.OverlapSphere(transform.position, radius);
foreach (Collider col in colliders)
{
Rigidbody rb = col.GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
if (rb != null)
{
rb.AddExplosionForce(force, transform.position, radius);
}
}
}
샘플 프로젝트 Github 저장소
'Develop > Unity' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Input System - Input Actions (0) | 2025.04.10 |
|---|---|
| InputSystem 기본 사용법 (0) | 2025.03.25 |
| 구글 계정 연동 (1) | 2025.02.28 |
| 2D 애니메이션, 이펙트 (1) | 2024.12.03 |
| Input System 사용시 UI 상호작용 안될때 (0) | 2024.11.18 |